Prescriptive Analytics
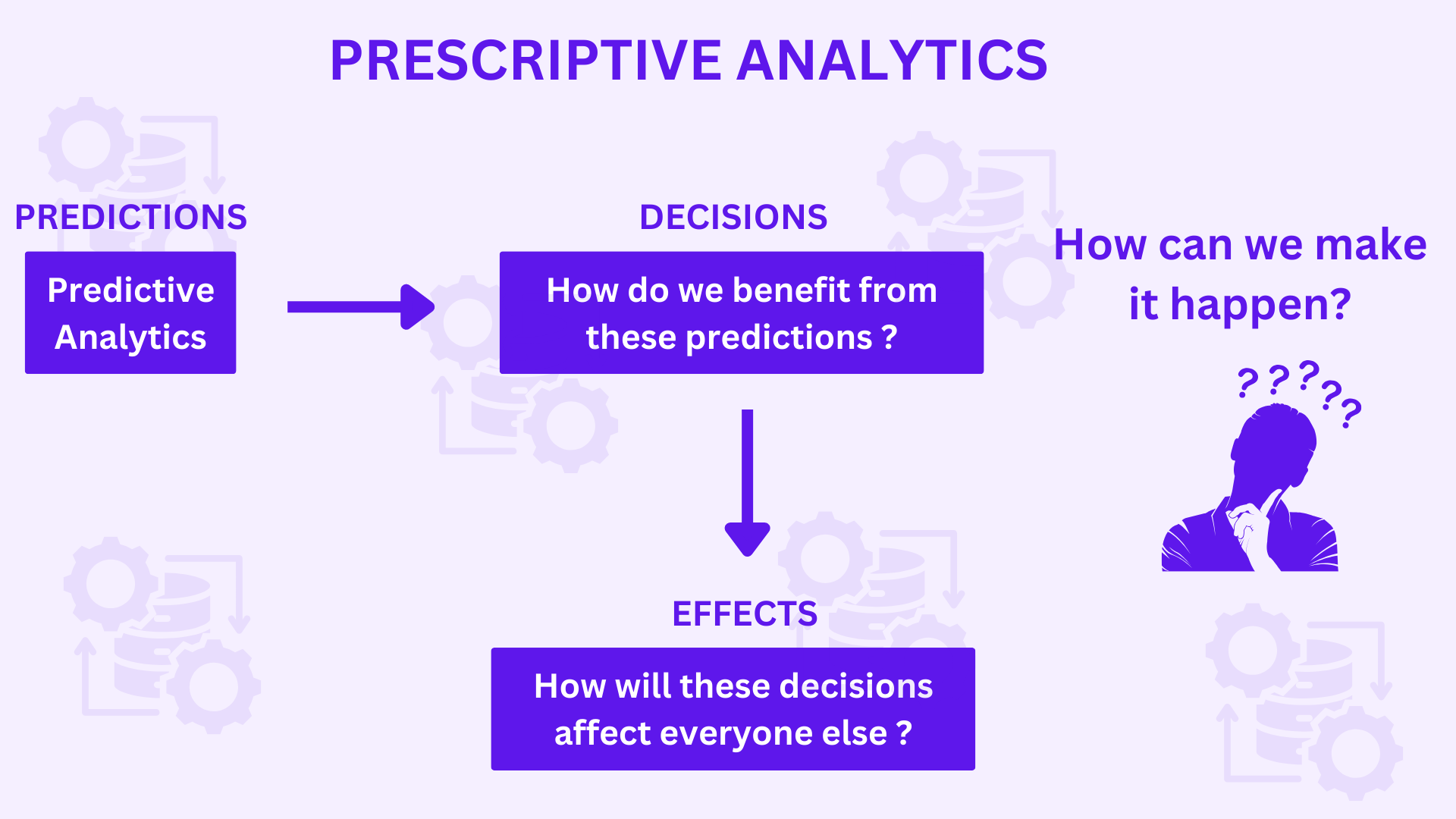
Prescriptive analytics is a type of data analytics that examines historical performance and trends to determine what needs to be done in order to meet future objectives. Despite the obvious benefits, corporate leaders should be aware that prescriptive analytics has drawbacks of its own.
Prescriptive analytics is applied in many fields, including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and retail. Prescriptive analytics can be used by a healthcare institution to recommend the best treatment plan for a patient, a financial institution to offer the best investment strategy or a manufacturing corporation to recommend the best production schedule.
How Prescriptive Analytics Works?
Prescriptive Analytics aims to answer the question, “How did we get here?” It uses artificial intelligence techniques like machine learning to understand and advance from the data it collects, evolving as it goes.
Machine learning enables the processing of massive amounts of data that are now available. When fresh or extra data becomes available, computer programming automatically change to make advantage of it, in a far faster and more complete procedure than human capacities could do.
Prescriptive Analytics works with predictive analytics, which involves the usage of statistics and modelling to forecast future performance based on current and past data. However, it goes a step further: It advises a future course of action based on the predictive analytics prediction of what is likely to happen.
Benefits of using prescriptive analytics:
Improved decision-making: Prescriptive analytics can help businesses to make better decisions by providing insights into the best course of action.
Increased efficiency: Prescriptive analytics can help businesses to automate tasks and optimize processes.
Reduced risk: Prescriptive analytics can help businesses to identify and mitigate risks.
Increased revenue: Prescriptive analytics can help businesses to increase sales and improve profitability.
Advantages of using Prescriptive Analytics:
Prescriptive analytics can break through the fog of current uncertainty and shifting conditions. It can aid in the prevention of fraud, the reduction of risk, the achievement of company objectives, and the creation of more loyal customers. When used correctly, it can assist organizations in making decisions based on extensively analyzed data rather than instinctively jumping to uninformed opinions.
Prescriptive analytics can simulate and show the probability of multiple outcomes, allowing organizations to better grasp the level of risk and uncertainty they face than relying on averages. It enables organizations to obtain a better knowledge of the possibility of worst-case outcomes and plan accordingly.
Disadvantages of using Prescriptive Analytics:
However, prescriptive analytics is not without flaws. Organizations can only be effective if they know what questions to ask and how to respond to the answers. As a result, it is only effective if its inputs are correct. If the input assumptions are incorrect, the output results will be incorrect.
This type of data analytics is only appropriate for short-term problems. This suggests that organizations should avoid using prescriptive analytics to make long-term decisions. This is because it becomes less trustworthy as more time is required.
Not all vendors of prescriptive analytics are created equal. As a result, organizations must carefully assess the technology and who supplies it. Some may bring genuine, measurable outcomes, whereas others promise enormous data but fail to deliver.
