Data Lakes
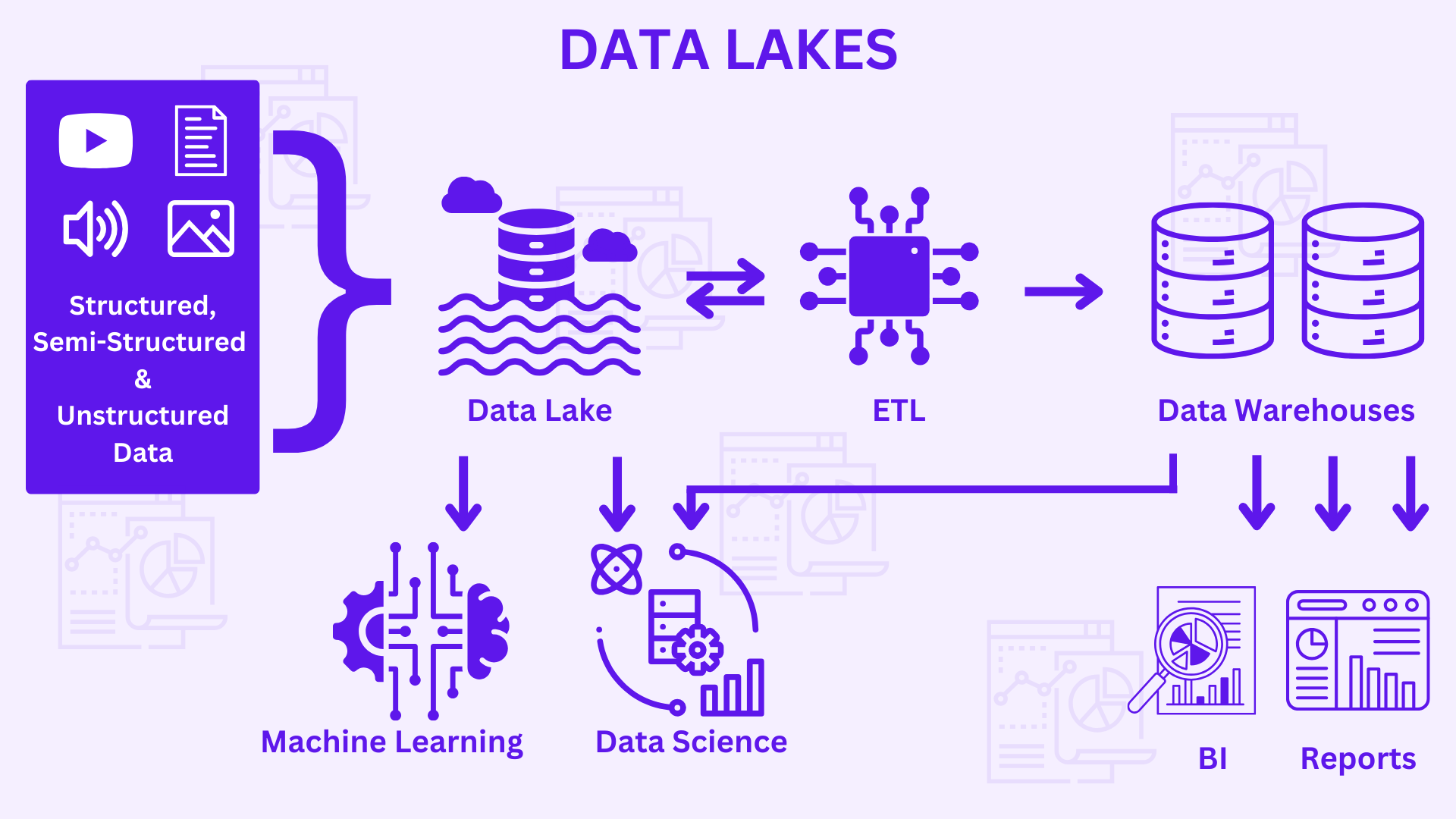
Data Lakes are a centralized repository that stores data in raw format. It can store structured, semi-structured and unstructured data. Data Lakes are only used to store the data that is not ready for analysis, and will be used to analyse the data in the future.
Advantages of Using a Data Lake
- It is capable of storing enormous volumes of data in its native format without the need for pre-processing. This facilitates the storage and management of many sorts of data.
- It can be used for data mining, machine learning, and business intelligence, among other things.
- It can assist organisations in gaining insights from their data that standard data warehouses cannot provide.
Ability of using Data Lakes
Powers Data Science & Machine Learning: With low latency, data lakes enable you to turn raw data into structured data that is ready for SQL analytics, data science, and machine learning. Raw data can be kept indefinitely for future use in machine learning and analytics at a reasonable cost.
Centralizes & forms catalogue of data: A centralised data lake addresses the problems associated with data duplication, numerous security regulations, and collaboration challenges providing downstream users with a single location to search for all data sources.
Quick & seamless integration across diverse data sources: A data lake can collect and store any sort of data, including batch and streaming data, video, image, binary files, and more. Furthermore, because the data lake serves as a landing zone for fresh data, it is always up to date.
Challenges of using Data Lakes
Data Lake Complexity: Data lakes can be difficult and costly to manage. They frequently comprise a range of data kinds that might be challenging to integrate and analyse. Furthermore, data lakes can be incredibly big, making it difficult to identify and access the data you require.
Data Lake Security: If not properly managed, data lakes might pose a security concern. They frequently contain sensitive information, such as client PII, financial information, and intellectual property. This data may be subject to hacking and other harmful parties.
Data Lake Scalability: To accommodate the expanding volume and variety of data, data lakes must be scalable. As businesses generate more data, they must be able to store it in a data lake without affecting performance.
