Information Action Value Chain
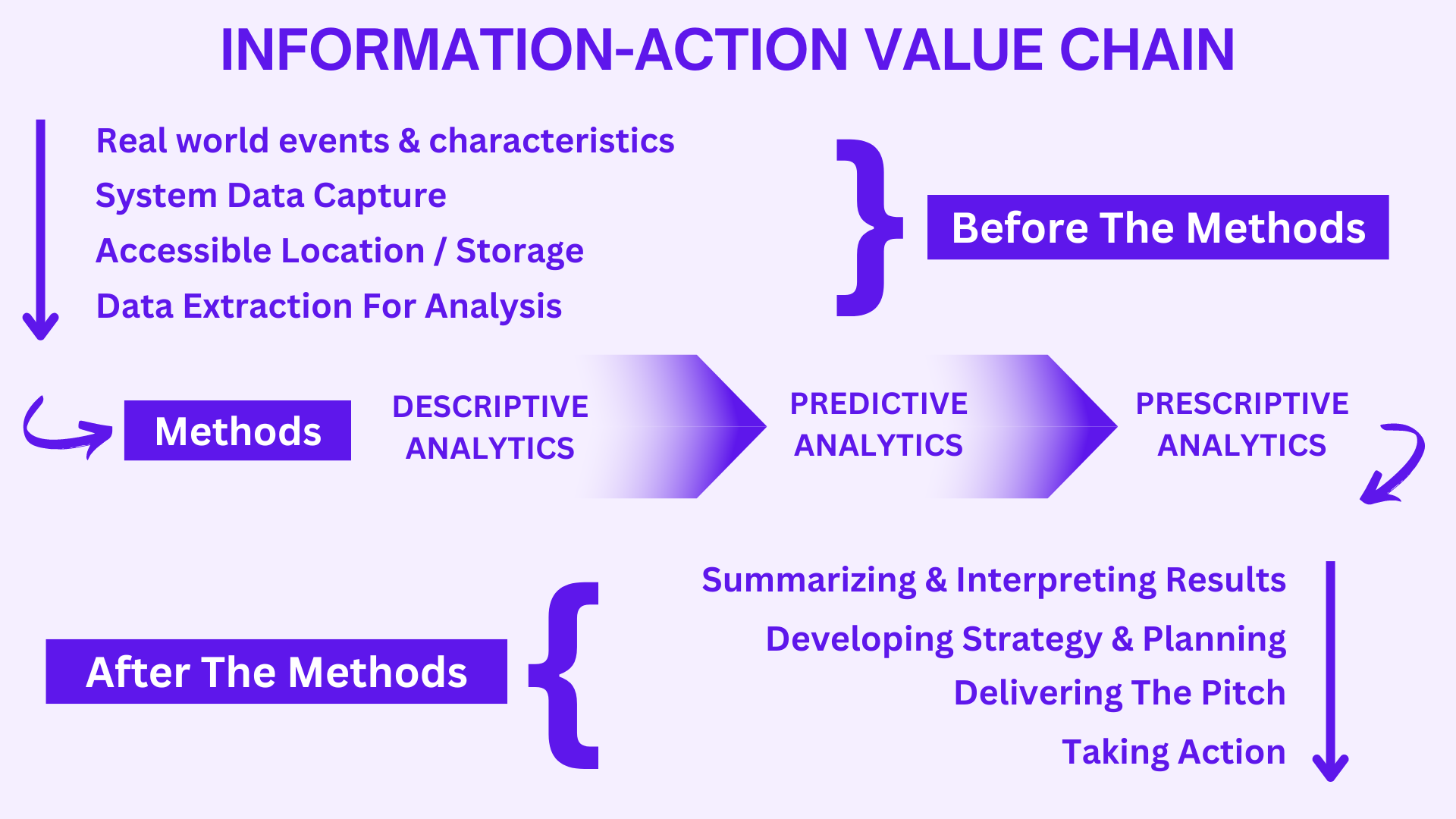
The information-action value chain is a framework that helps organizations understand how information can be used to create value. It basically consists of three parts, namely before the methods, the methods and after the methods.
Before the methods describes the data being generated, captured, stored and then using the particular data for being analysed.
- Real world events & characteristics: Everything starts with this real world, and the events & circumstances happening here.
- System Data Capture: Events need to be captured by source systems & then turned into data.
- Accessible Location / Storage: Data from source systems can be brought into one common location for access & storage.
- Data Extraction for Analysis: Extracting only the data we need for analysis.
Now comes the methods through which the data extracted will be analysed. There are mainly three methods:
- Descriptive Analytics: Descriptive Analytics helps us describe what things look like or what happened in the past. It can take forms of simple aggregations or cross tabulations data. Simple statistical measures like means, median 7 standard deviations are used. In sophisticated measures, distributions, confidence intervals & hypotheses tests are used. Know More about descriptive analytics in our detailed blog here.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive Analytics helps us take what we know about what happened in the past, & use that information to help us predict what will happen in the future. This analytical method involved application of advanced statistical methods or other numeric techniques such as linear regression or logistic regression. Know More about predictive analytics in our detailed blog here.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Prescriptive Analytics helps explicitly link analysis to decision making by making recommendations on what we should do or what choice we should make to achieve a certain outcome. This analytical method uses predictions generated during Predictive Analytics and then uses & involves integration of numerical optimisation techniques with business rules and even financial models. Know More about prescriptive analytics in our detailed blog here.
Also, there are two more analytical methods, namely Real Time Analytics & Diagnostic Analytics. I will also cover these two in my coming blog.
After applying the analytical methods for analysing the data, now comes the after methods processes for interpreting the results, delivering and taking actions for the stakeholders. The steps include:
- Summarising & Interpreting Results: This process of organizing and presenting the findings of an analysis in a concise and easy-to-understand way. This can be done through tables, charts, graphs, or written descriptions. Interpreting Result can be done by considering the research questions, the data, and the analytical methods used. The following are some important considerations when summarizing and interpreting results:
- The audience for the results: Who will be reading or hearing the results? What level of detail is appropriate?
- The purpose of the analysis: What are the research questions that the analysis was designed to answer?
- The data: What data was collected? What are the limitations of the data?
- The analytical methods: What analytical methods were used? How reliable and valid are the methods?
- Developing Strategy & Planning: After using the analytical methods, it can be used to develop strategy and planning by providing insights into the current situation, identifying opportunities and threats, and assessing the feasibility of different options. By using analytical methods, organizations can develop more informed and effective strategies and plans. Here are some additional benefits of using analytical methods in strategy and planning:
- Improved decision-making: By using analytical methods to gather and analyse information, organizations can make better decisions about their future direction.
- Increased efficiency: By identifying and eliminating waste, organizations can improve their efficiency and reduce costs.
- Enhanced customer focus: By understanding customer needs, organizations can provide a more personalized and relevant experience.
- Increased innovation: By identifying new opportunities, organizations can innovate and stay ahead of the competition.
- Delivering The Pitch: This generally involves the steps regarding the clarity, simplicity, values & qualities the analysis report contains after preforming the complete information chain. This includes the analyst stand towards the stakeholders needs for their requirements in their business.
- Taking Action: This step is used to support decision-making by providing insights into the likely outcomes of different choices. For example, a company might use analytical methods to help it decide whether to enter a new market or launch a new product. These can be the actions taken on the basis of analysing the required data for the stakeholder’s requirement.
The information-action value chain is a continuous process. As new data is collected, it is fed back into the process to generate new insights and drive new actions.
Here are some examples of how organizations are using the information-action value chain to create value:
- A retailer uses data from its point-of-sale systems to track customer behaviour and identify trends. This information is used to optimize inventory levels, target marketing campaigns, and improve customer service.
- A manufacturing company uses data from its sensors to monitor the performance of its equipment. This information is used to identify potential problems before they cause outages, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
- A healthcare provider uses data from electronic health records to identify patients who are at risk for severe diseases. This information is used to provide preventive care and improve patients’ health.
The information-action value chain is a powerful tool that can help organizations improve their decision-making, identify new opportunities, and create value.
Here are some of the benefits of using the information-action value chain:
- Improved decision-making: By using data to inform their decisions, organizations can make better choices about how to allocate resources, develop new products and services, and improve customer service.
- Increased efficiency: By identifying and eliminating waste, organizations can improve their efficiency and reduce costs.
- Enhanced customer experience: By using data to understand customer needs, organizations can provide a more personalized and relevant experience.
- Increased innovation: By using data to identify new opportunities, organizations can innovate and stay ahead of the competition.
If you are looking to improve your business or organization’s performance, the information-action value chain is a framework that you should consider.
